Page 2 - ch 20
P. 2
Module - V Kargil Conflict - 1999
Major Wars Post
Independence
Note
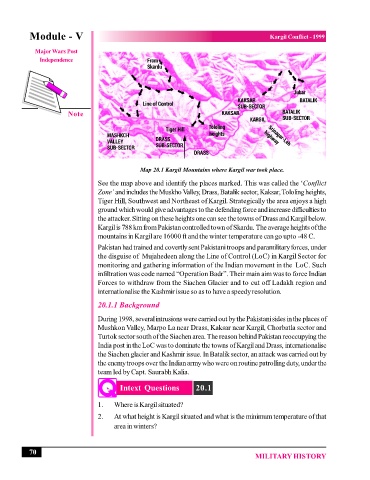
Map 20.1 Kargil Mountains where Kargil war took place.
See the map above and identify the places marked. This was called the ‘Conflict
Zone’ and includes the Muskho Valley, Drass, Batalik sector, Kaksar, Tololing heights,
Tiger Hill, Southwest and Northeast of Kargil. Strategically the area enjoys a high
ground which would give advantages to the defending force and increase difficulties to
the attacker. Sitting on these heights one can see the towns of Drass and Kargil below.
Kargil is 788 km from Pakistan controlled town of Skardu. The average heights of the
mountains in Kargil are 16000 ft and the winter temperature can go upto -48 C.
Pakistan had trained and covertly sent Pakistani troops and paramilitary forces, under
the disguise of Mujahedeen along the Line of Control (LoC) in Kargil Sector for
monitoring and gathering information of the Indian movement in the LoC. Such
infiltration was code named “Operation Badr”. Their main aim was to force Indian
Forces to withdraw from the Siachen Glacier and to cut off Ladakh region and
internationalise the Kashmir issue so as to have a speedy resolution.
20.1.1 Background
During 1998, several intrusions were carried out by the Pakistani sides in the places of
Mushkon Valley, Marpo La near Drass, Kaksar near Kargil, Chorbatla sector and
Turtok sector south of the Siachen area. The reason behind Pakistan reoccupying the
India post in the LoC was to dominate the towns of Kargil and Drass, internationalise
the Siachen glacier and Kashmir issue. In Batalik sector, an attack was carried out by
the enemy troops over the Indian army who were on routine patrolling duty, under the
team led by Capt. Saurabh Kalia.
Intext Questions 20.1
1. Where is Kargil situated?
2. At what height is Kargil situated and what is the minimum temperature of that
area in winters?
70
70
MILITARY HISTORY