Page 6 - Lesson 5.xps
P. 6
MODULE-2 Physical and Physiological Aspects of Physical Education
Dimension of Physical
Education and Yog Intensity of Activity: amount of physical power that the body uses during
the activity is known as intensity of activity. It may also be calculated by
the amount of force or energy exerted in relation to time. Example: intensity
in running can be measured by calculating the speed which may further be
illustrated in units as m/sec or km/hr. in weight lifting intensity can be
measured in Weight in Kgs or in tons etc.
Volume of the Activity: Work done during exercise or activity is known as
Note volume of activity. It can be measured by duration, distance and frequency
of an activity. Example in running activity volume can be measured in
second, minutes, hours or in meter, km. etc. in weight lifting volume can be
measured in repetition / time.
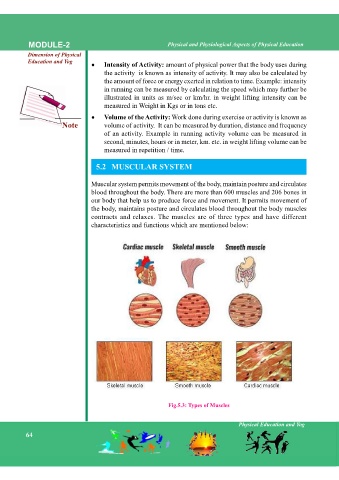
5.2 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
Muscular system permits movement of the body, maintain posture and circulates
blood throughout the body. There are more than 600 muscles and 206 bones in
our body that help us to produce force and movement. It permits movement of
the body, maintains posture and circulates blood throughout the body muscles
contracts and relaxes. The muscles are of three types and have different
characteristics and functions which are mentioned below:
Fig.5.3: Types of Muscles
Physical Education and Yog
64